Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is an anxiety disorder caused by very stressful, frightening or distressing events.
“Shell Shock” and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
The origins of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder date back to World War One. As the magnitude of wartime gun battles and incidences of shelling attacks increased, soldiers began returning from battle with a multitude of conditions with no apparent cause, ranging from paralysis and panic attacks to nervous disorders and the inability to eat or sleep. Physicians of the time categorised the condition as an unexplained heart disorder.
Scottish cardiologist and RCP fellow Sir James Mackenzie, a pioneer in the study of arrhythmia, was called to treat soldiers as a consultant to the Military Heart Hospital. He began treating soldiers for PTSD, without fully understanding what it really was. He believed that “shell shock” or “Soldiers’ Heart” occurred because the physical burden and extreme exhaustion of war enabled toxic bacteria to form in the central nervous system.
His recommendation of outdoor games, exercise and leisurely activities to promote healing was a departure from other therapies, as was his belief that the condition was not cardiac in nature.
Symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
Someone with PTSD often relives the traumatic event through nightmares and flashbacks, and may experience feelings of isolation, irritability and guilt.
They may also have problems sleeping, such as insomnia, and find concentrating difficult.
These symptoms are often severe and persistent enough to have a significant impact on the person's day-to-day life.
Causes of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
Any situation that a person finds traumatic can cause PTSD.
These can include:
serious road accidents
violent personal assaults, such as sexual assault, mugging or robbery
serious health problems
childbirth experiences
PTSD can develop immediately after someone experiences a disturbing event, or it can occur weeks, months or even years later. PTSD is estimated to affect about 1 in every 3 people who have a traumatic experience, but it's not clear exactly why some people develop the condition and others do not.
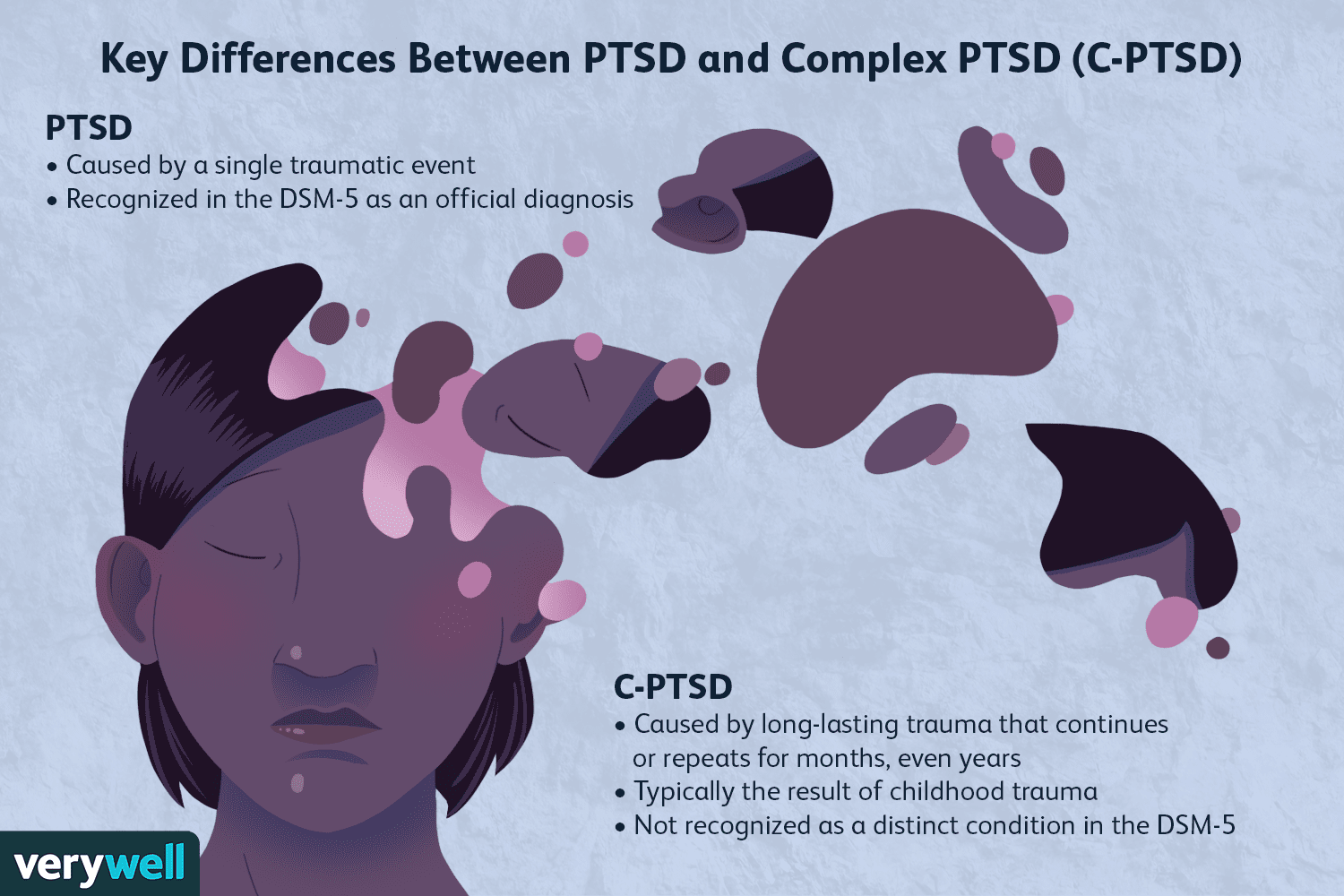
Complex post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
People who repeatedly experience traumatic situations, such as severe neglect, abuse or violence, may be diagnosed with complex PTSD.
Complex PTSD can cause similar symptoms to PTSD and may not develop until years after the event.
It's often more severe if the trauma was experienced early in life, as this can affect a child's development.
When to get medical advice
It's normal to experience upsetting and confusing thoughts after a traumatic event, but most people improve naturally over a few weeks.
You should see a GP if you or your child are still having problems about 4 weeks after the traumatic experience, or if the symptoms are particularly troublesome.
Here at Vitalis we are happy to see patients who may be suffering from PTSD. We can give you time and space in our calming city centre clinic to get to the root of your problem. We may need to refer you to mental health specialists for further assessment and treatment. We also have a list of mental health practitioners that may be useful: https://vitalishealth.co.uk/mental-health-directory
How post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is treated
PTSD can be successfully treated, even many years after a traumatic event.
Treatment depends on the severity of symptoms and how soon they occur after the traumatic event. Each person is different and may need anumber of approaches.
Any of the following treatment options may be recommended:
Exercise, Yoga, meditation, mindfulness
Antidepressants – such as paroxetine or sertraline
psychological therapies – such as trauma-focused cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) or eye movement desensitisation and reprocessing (EMDR)
Body work and therapeutic massage can help many people who have found relationships and social connection difficult.
Ultimately, finding an experienced therapist with whom you have a good raport is crucial to healing.